Summary of a review of literature on how to develop a young Olympic weightlifter.
Who
Young Olympic weightlifters
Design
Review of the literature
Outcome measures
- training prescription
- exercise selection and progression
- physical capacity
- skill development
Main results
- Progression scheme of a weightlifter’s development:
- physical capacity:
- start with motor control and exercises performed at body weight
- second move to basic strength development
- then maximum strength exercises can be used
- explosive strength can follow
- training prescription:
- training frequency goes from low to high
- repetition velocity from low (slow) to high (fast)
- intensity goes from low (light) to high (heavy)
- repetition volume goes from high (many reps) to low (1-3 reps)
- exercise selection:
- from athletic motor skill competencies (popular movements used in many sports)
- then foundational strength exercises
- after that, weightlifting derivatives
- the last stage would be weightlifting derivatives and full lifts (snatch, clean & jerk)
- skill development:
- from movement competency
- to technical competency
- to technical autonomy
- to technical refinement
- physical capacity:
Progression
First
Second
Then
Last
Physical capacity
Progression
First
motor control and body weight exercises
Second
basic strength
Then
maximum strength
Last
explosive strength
Training prescription
Progression
First
training frequency from low to high
Second
repetition velocity from low to high
Then
Intensity from low to high
Last
repetition volume from high to low
Exercise prescription
Progression
First
foundational movements (athletic motor skills)
Second
foundational strength
Then
weightlifting derivatives
Last
weightlifting derivatives and full lifts
Skill development
Progression
First
movement competency
Second
technical competency
Then
technical autonomy
Last
technical refinement
Progression
Athletic motor skill competencies
Foundation strength
Weightlifting derivatives (Level 1)
Weightlifting derivatives (Level 2)
Full lifts
Snatch
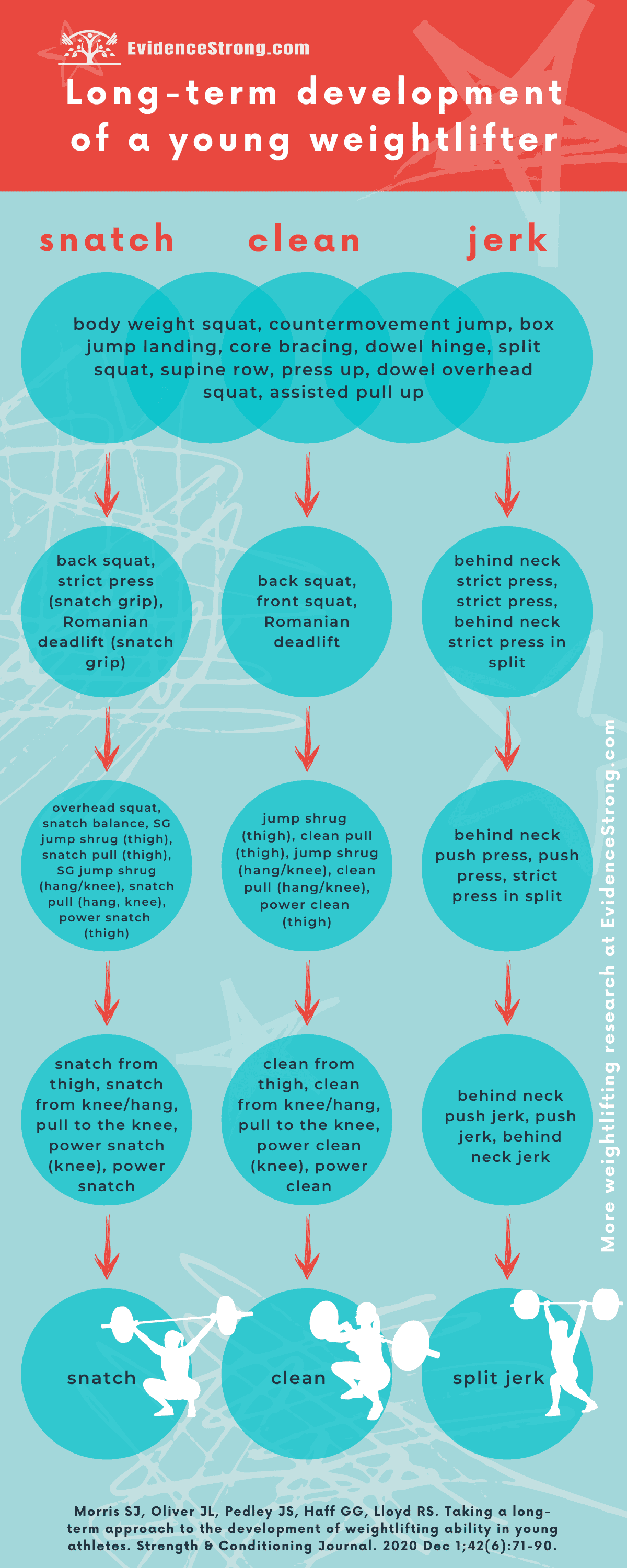
Progression
Athletic motor skill competencies
body weight squat - countermovement jump - box jump landing - core bracing - dowel hinge - split squat - supine row - press up - dowel OH press - assisted pull up
Foundation strength
back squat - strict press (snatch grip) - Romanian deadlift (snatch grip)
Weightlifting derivatives (Level 1)
overhead squat - snatch balance - snatch grip jump shrug (thigh) - snatch pull (thigh) - snatch grip jump shrug (hang/knee) - snatch pull (hang/knee) - power snatch (thigh)
Weightlifting derivatives (Level 2)
snatch from thigh - snatch from knee/hang - pull to the knee (snatch grip) - power snatch (knee) - power snatch
Full lifts
snatch
Clean
Progression
Athletic motor skill competencies
body weight squat - countermovement jump - box jump landing - core bracing - dowel hinge - split squat - supine row - press up - dowel OH press - assisted pull up
Foundation strength
back squat - front squat - Romanian deadlift
Weightlifting derivatives (Level 1)
jump shrug (thigh) - clean pull (thigh) - jump shrug (hang/knee) - clean pull (hang/knee) - power clean (thigh)
Weightlifting derivatives (Level 2)
clean from thigh - clean from knee/hang - pull to the knee - power clean (knee) - power clean
Full lifts
clean
Split jerk
Progression
Athletic motor skill competencies
body weight squat - countermovement jump - box jump landing - core bracing - dowel hinge - split squat - supine row - press up - dowel OH press - assisted pull up
Foundation strength
behind neck strict press - strict press - behind neck strict press in split
Weightlifting derivatives (Level 1)
behind neck push press - push press - strict press in split
Weightlifting derivatives (Level 2)
behind neck push jerk - push jerk - behind neck jerk
Full lifts
split jerk
Take home message
For a clinician & coach
Young Olympic weightlifters should be exposed to weightlifting training from less demanding and lighter movements to more challenging and heavier variations with more repetitions in a slower pace at the beginning.
For a parent
Young Olympic weightlifters should be exposed to weightlifting training from less demanding and lighter movements to more challenging and heavier variations.
For an athlete
Young Olympic weightlifters should be exposed to weightlifting training from less demanding and lighter movements to more challenging and heavier variations.
Interview with the author of the original article
Steph Morris is a PhD student in Youth Weightlifting and lecturer in Strength & Conditioning at Cardiff Metropolitan University. She is Welsh Rowing S&C Coach and Youth Physical Development (YPD) S&C Coach.
Original article
Morris SJ, Oliver JL, Pedley JS, Haff GG, Lloyd RS. Taking a long-term approach to the development of weightlifting ability in young athletes. Strength & Conditioning Journal. 2020 Dec 1;42(6):71-90.