Summary of an article on glycogen content before and immediately after a high intensity weightlifting session in elite powerlifters and Olympic weightlifters.
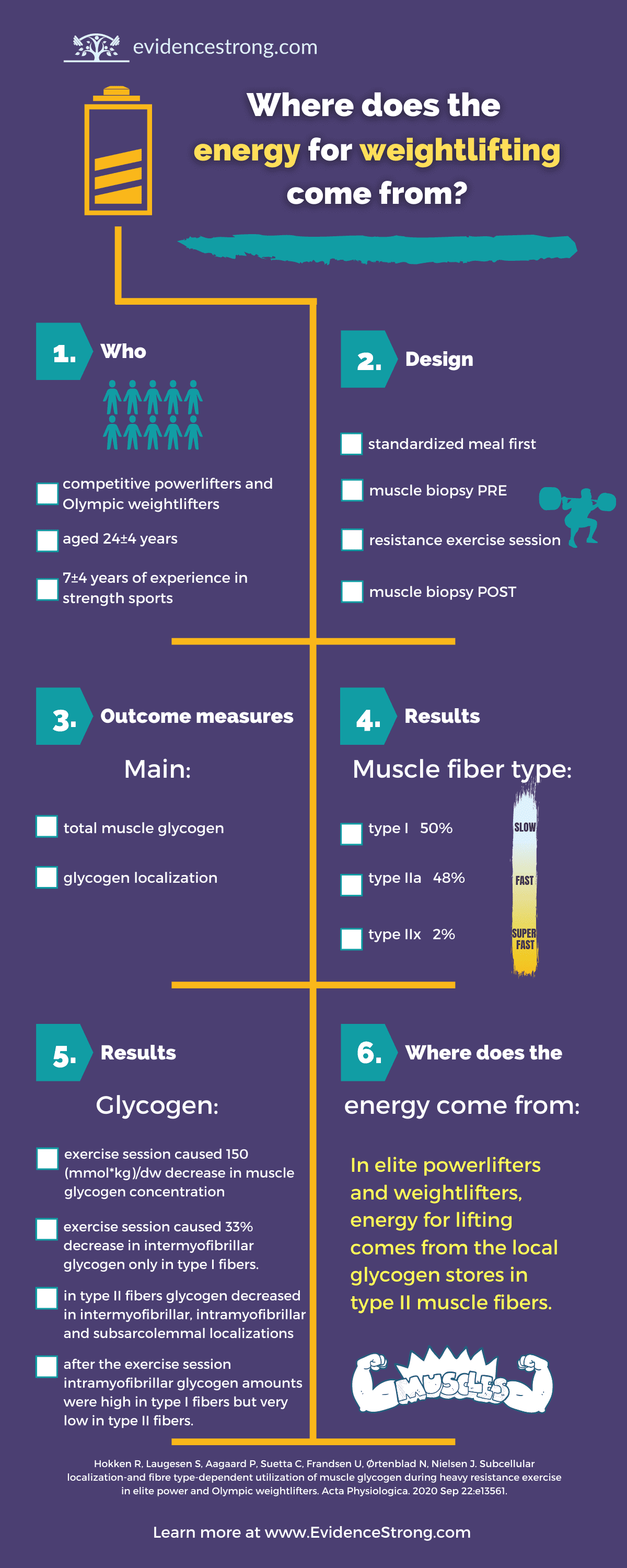
Who
10 male competitive power and Olympic weightlifters aged 24 ± 4 years with average body weight of 95 ±8 kg, 7 ± 4 years of experience in strength sports and personal bests for squat at 210 ± 25, bench 150 ± 18, and deadlift 243 ± 29 kg (Denmark).
Design
Experimental study. Participants ate a standardized meal (~560 kcal) and 1.5 hour later performed high intensity resistance exercise session:
- warm-up (involving dynamic stretching)
- 3 lower body exercises (up to 70-75% of RM):
- back squat
- deficit deadlift (10 cm)
- rear foot elevated split squat
2 muscle biopsies: before and immediately after the exercise session
Outcome measures
- body composition via DEXA
- muscle biopsy from the middle portion of vastus lateralis muscle:
- myosin heavy chain (MHC) distribution
- total mucle glycogen content
- subcellular glycogen localization
- muscle lactate
- fiber type
Main results
myosin heavy chain distribution was 50% MHCI, 48% MHCIIa and 2% MHCIIx
muscle glycogen concentration decreased from 398 (mmol kg dw-1) before the exercise session to 249 after the exercise session (change 150)
exercise session caused 33% decrease in intermyofibrillar glycogen only in type I fibers. In type II fibers glycogen decreased in intermyofibrillar, intramyofibrillar and subsarcolemmal localizations. After the exercise session intramyofibrillar glycogen amounts were high in type I fibers but very low in type II.
intermyofirillar glycogen amounts were around 80% of all glycogen content in both fibers types (10% intramyofibrillar, 10% subsarcolemmal).
muscle lactate concentration increased from 7.3 (mmol kg dw-1) before the exercise session to 32.1 after the exercise session (change 340%)
after the exercise, glycogen particles were smaller.
Also, in most glycogen-depleted fibers after exercise session, small crystal-like structures appeared in intermyofirillar and subsarcolemmal spaces.
Take home message
Original article
Hokken R, Laugesen S, Aagaard P, Suetta C, Frandsen U, Ørtenblad N, Nielsen J, Nielsen J. Subcellular localization-and fibre type-dependent utilization of muscle glycogen during heavy resistance exercise in elite power and Olympic weightlifters. Acta Physiologica. 2020 Sep 22:e13561.