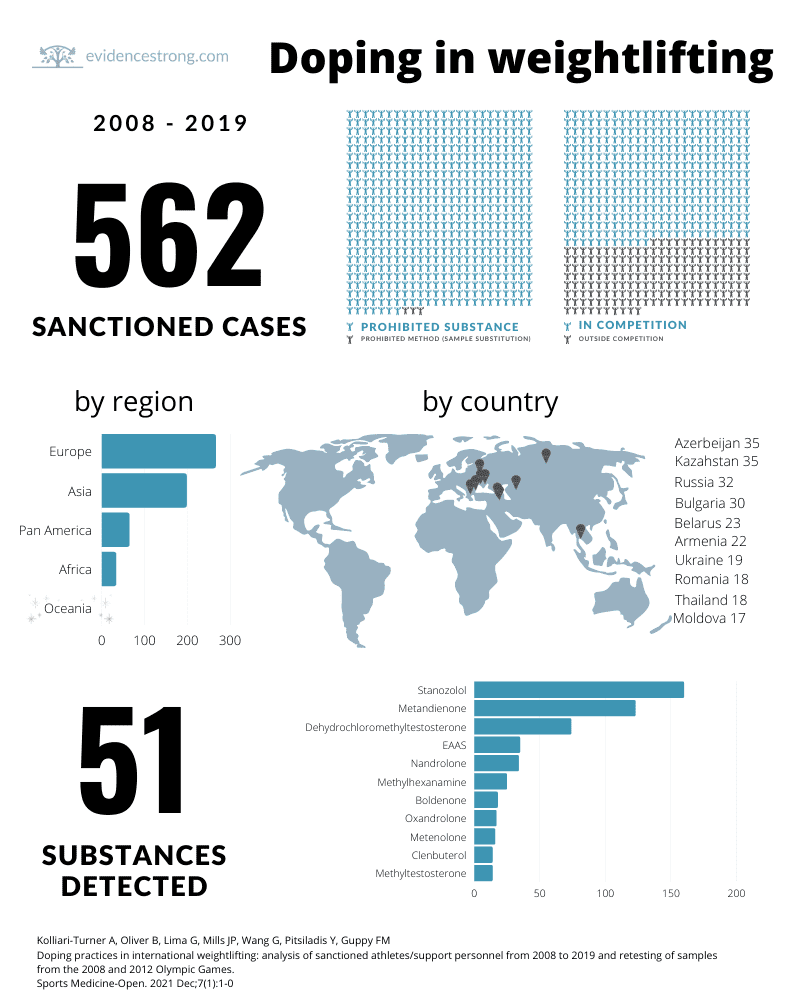
Summary of doping practices in weigthlifting between 2008 and 2019, including results of sample re-testing from 2008 Beijing and 2012 London Olympics.
Who
562 sanctioned athletes (83 federations).
Design
Analysis of 2008-2019 IWF data on anti-doping violations.
Outcome measures/tests
- substance detection:
- parent compound of noted metabolites
- EAAS used for markers, their precursors or masking agents
- anti-doping rules violation.
EAAS – "markers of endogenous usage including androsterone,testosterone, epitestosterone, etiocholanolone, 5α-androstane-3α,17β-diol (5αAdiol), and 5β- androstane-3α,17β-diol (5βAdiol)"
Main results
- 559 athletes were sanctioned for the use of prohibited substances, 3 athletes for prohibited method (urine or blood substitution)
- ⅔ of sanctions were in-competion tests.
- 51 substances detected.
- The most detected substances were (% in-competition):
- Dehydrochloromethyltestosterone (89%)
- markers indicating EAAS usage (76%),
- Metenolone (100%),
- Methylhexanamine (100%)
- Methyltestosterone (71%)
- Nandrolone (86%)
- Stanozolol
- Metandienone
- Sanctions by region:
- Asia 199
- Europe 267
- Africa 34
- Pan America 65
- Oceania 0
- Proportions of EAAS detected differed between regions.
- Countries with the most sanctions:
- Azerbaijan 35
- Kazakhstan 35
- Russia 32
- Bulgaria 30
- Belarus 23
- Armenia 22
- Ukraine 19
- Romania 18
- Thailand 18
- Moldova 17
- Re-testing of 2008 and 2012 Olympic Games’ samples resulted in:
- 61 athletes sanctioned (13 countries)
- 64% of sanctioned athletes were medalists in 2008 Olympics and 50% in 2012 Olympics.
- All athletes from Romania and Moldova who competed in 2012 Olympics generated positive re-testing results.
- All medalists from Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Belarus, Romania, Azerbaijan, Armenia and Moldova re-tested positive after 2012 Olympics.
- Weight categories that had at least 2 medalist re-test positively:
- 2008 Olympics: W 48kg, W 69kg, W 75kg, W 75+kg, M 94kg
- 2012 Olympics: W 53kg, W 63kg, W 69kg, W 75kg (all medalists), M 94kg (all medalist; 6 out of first 10 athletes produced positive re-test results)
- 94 prohibited substances detected in re-tested samples
- 83% of sanctions had Dehydrochloromethyltestosterone or Stanozolol
- Countries with the most positive re-test (with the main reason):
- Kazakhstan 10 (Stanozolol 67%)
- Russia 10 (Dehydrochloromethyltestosterone 71%)
- Belarus 8 (Dehydrochloromethyltestosterone 44%, Stanozolol 44%)
- Azerbaijan 6 (Dehydrochloromethyltestosterone 67%)
- Armenia 5 (Dehydrochloromethyltestosterone 50%, Stanozolol 50%)
- Turkey 5 (Stanozolol 71%)
- Romania 4 (Metenolone 40%, Stanozolol 40%)
- Ukraine 4 (Dehydrochloromethyltestosterone 100%)
- China 3 (Growth Hormone-releasing Peptide-2 75%)
- Moldova 3 (Dehydrochloromethyltestosterone 67%)
- These numbers may change due to WADA and ITA investigations still in progress (41 hidden cases, 10 possible cases, 130 unprocessed samples).
Take home message
Original article
Kolliari-Turner A, Oliver B, Lima G, Mills JP, Wang G, Pitsiladis Y, Guppy FM. Doping practices in international weightlifting: analysis of sanctioned athletes/support personnel from 2008 to 2019 and retesting of samples from the 2008 and 2012 Olympic Games. Sports Medicine-Open. 2021 Dec;7(1):1-0.
IWF list: Athletes sanctioned for valiation of anty-doping roles.